1- Introduction
The DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface) communications protocol is an international standard defined by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) in IEC 62386. It is a communications protocol created to control lighting systems.
DALI is an open protocol, which means it is compatible with products from different manufacturers. This simplifies the installation and maintenance of public lighting systems. DALI is a bidirectional protocol, which means it allows communication between the controller and the luminaires. This makes it possible to collect data on the luminaires, such as ON/OFF of the luminaire, energy consumed, temperature, voltage, intensity, cos Phi, power...
2- DALI bus and wiring principle
A specific DALI Bus power supply is required. It is continuous and has a voltage of approximately 16V. However, the voltage drop must not exceed 2V. The power intensity is defined by the number of DALI devices present on the BUS.
The advantage of the DALI Bus consists of the non-polarity of the control wires, unlike other systems (0-10V, DMX, etc.).
On installations, to pass power and control (DALI), 1.5mm² 5G cable is very often used.
3- DALI wiring topology options
The lengths of the DALI Bus can vary depending on the diameter of the cable:
- 150 meters in 0.75 mm² ;
- 300 meters in 1.5 mm² ;
The other advantage is being able to connect DALI devices in the direction you want (in the form of a Bus or star for example).
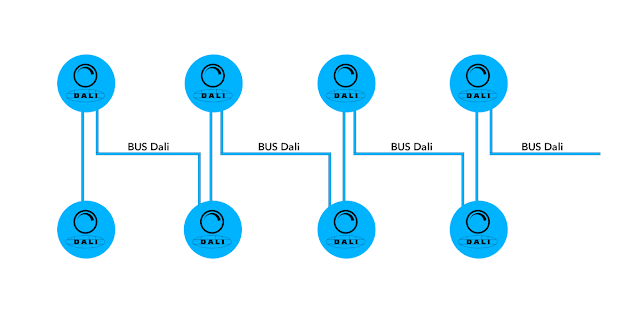
3.1- Option 1: Bus type wiring
On a DALI Bus, it is possible to address up to 64 DALI devices, group them into a maximum of 16 groups and then create up to 16 scenes.
3.2- Option 2: star wiring
In star cabling, within this limit (of 64 devices), it is not necessary to have a centralized management system. Once the lighting devices have been configured (definition of addresses, groups, scenes) via an interface (often USB which is temporarily connected to the DALI Bus), the system is perfectly autonomous.
4- Versions of the DALI protocol
There are two versions of the DALI protocol:
DALI version 1: This is the first version of the protocol, released in 2000. It is mainly used in commercial and industrial applications.
DALI version 2: This is the second version of the protocol, published in 2012. It brings many improvements compared to version 1, including:
- Support for new device types, such as light sensors and occupancy detectors.
- The ability to create lighting scenarios.
- Support for security and reliability.
DALI version 2 is the most common version today. It is used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Residential lighting
- Commercial lighting
- Industrial lighting
- Public lighting
SEE MORE
5- Advantages of DALI for public lighting
DALI offers a number of benefits for street lighting, including:
Energy efficiency: DALI allows precise control of the brightness of luminaires, which can lead to significant energy savings.
Flexibility: DALI allows you to create complex lighting programs, such as brightness changes depending on the time of day or the presence of people.
Safety: DALI allows the status of luminaires to be monitored, which can help improve public safety.
Durability: DALI is a robust protocol that can withstand harsh weather conditions.
6- DALI applications for public lighting
DALI can be used in a variety of street lighting applications including:
Street lighting: DALI can be used to control the brightness of street lights to adapt lighting to traffic and safety conditions.
Lighting for parks and gardens: DALI can be used to create dynamic lighting programs that highlight landscapes.
Public building lighting: DALI can be used to control interior lighting in public buildings, such as schools and hospitals.
7- Conclusion
DALI is an advanced communications protocol that offers many benefits for street lighting. It is efficient, flexible, safe, and durable, making it an ideal choice for a variety of applications.